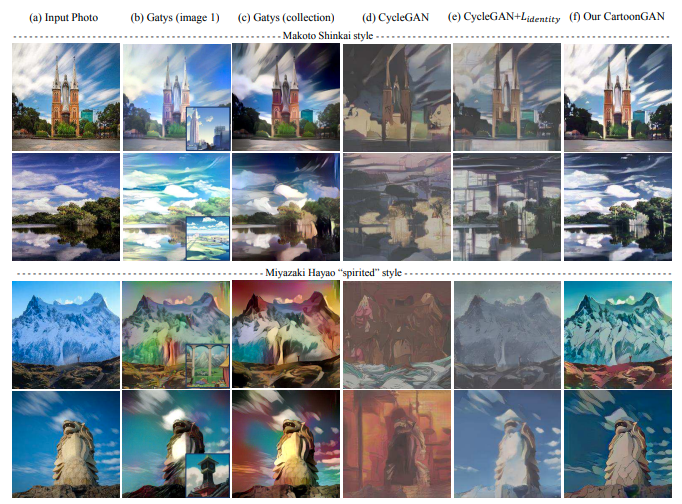
CartoonGAN- Generative Adversarial Networks for Photo Cartoonization
An overview of the paper “CartoonGAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Photo Cartoonization”. The authors propose a novel approach to transform photos of real world scenes into cartoon style images. All images and tables in this post are from their paper.
Introduction
Manually recreating real-world scenes in cartoon styles is very laborious and involves substantial artistic skills. To obtain high-quality cartoons, artists have to draw every single line and shade each color region of target scenes. Meanwhile, existing image editing software/algorithms with standard features cannot produce satisfactory results for cartoonization. Therefore, specially designed techniques that can automatically transform real world photos to high-quality cartoon style images are very helpful and for artists, tremendous amount of time can be saved so that they can focus on more creative work. Two novel losses suitable for cartoonization are proposed: (1) a semantic content loss and (2) an edge-promoting adversarial loss for preserving clear edges.
A GAN framework consists of two CNNs. One is the generator which is trained to produce output that fools the discriminator. The other is the discriminator
which classifies whether the image is from the real target manifold or synthetic.
CartoonGAN Architecture
In CartoonGAN, the generator network is used to map input images to the cartoon manifold. Cartoon stylization is produced once the model is trained. Complementary to the generator network, the discriminator network
is used to judge whether the input image is a real cartoon image.
Loss function
The loss function consists of two parts: (1) the adversarial loss
which drives the generator network to achieve the desired manifold transformation, and (2) the content loss
, which preserves the image content during cartoon stylization. They then use a simple additive form for the loss function:
.
Adversarial Loss )
Its value indicates to what extent the output image of the generator looks like a cartoon image. In CartoonGAN, the goal of training the discriminator
is to maximize the probability of assigning the correct label to
, the cartoon images without clear edges (i.e.,
) and the real cartoon images (i.e.,
), such that the generator
can be guided correctly by transforming the input to the correct manifold.
Content Loss )
In addition to transformation between correct manifolds, one more important goal in cartoon stylization is to ensure the resulting cartoon images retain semantic content of the input photos. In CartoonGAN, we adopt the high-level feature maps in the VGG network pre-trained, which has been demonstrated to have good object preservation ability.
Semantic content loss is defined using the l1 sparse regularization of VGG feature maps between the input photo and the generated cartoon image. This is due to the fact that cartoon images have very different characteristics (i.e., clear edges and smooth shading) from photos. We observe that even with a suitable VGG layer that intends to capture the image content, the feature maps may still be affected by the massive style difference. Such differences often concentrate on local regions where the representation and regional characteristics change dramatically. l1 sparse regularization is able to cope with such changes much better than the standard l2 norm.
Ouput from CartoonGAN.